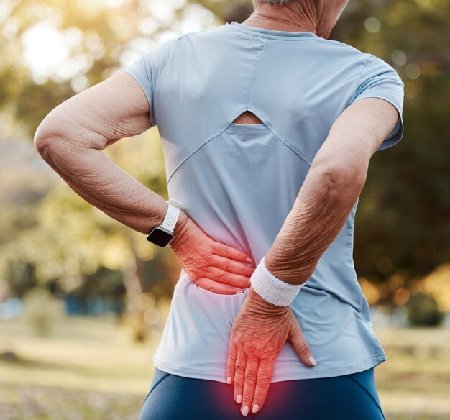
A disc prolapse, also known as a herniated disc, is a medical condition that occurs when the soft, gel-like center of an intervertebral disc protrudes or leaks through the tough outer layer. The intervertebral discs are located between the vertebrae of the spine and act as cushions, providing flexibility and shock absorption to the spinal column. When a disc herniates, it can put pressure on nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in the affected area.
The most common cause of disc prolapse is aging, as the discs naturally degenerate and lose their water content over time, making them more susceptible to injury. However, other factors such as sudden trauma, improper lifting techniques, or repetitive stress on the spine can also contribute to disc herniation.